About 80% of people over 55 experience manifestations of various back diseases, should not neglect the faces of younger age categories. Therefore, one of the most common diseases in the spinal spine-posterochondrosis of the lumbar spine is also found in patients aged 25 to 45 years. Until 16 to 25 -year -olds are becoming increasingly symptoms and causes of this extremely unpleasant disease. The question becomes logical about whether it is possible to interrupt the trend of the number of patients in general and what to do to each person for preventive purposes not to become a victim of this pathology?

Symptoms
With insufficient attention to this disease, premature diagnosis, its treatment is difficult as diseases or secondary complications occur. As a natural continuation of pathology, osteochondrosis begins to progress. Its treatment is not always effective and, at the grip or an incorrectly prescribed therapeutic course, a risk of disability occurs. Another characteristic problem is the appearance of intervertebral hernias, which is accompanied by unbearable painful sensations. Every day, the chances of getting rid of irrevocable hernia are getting less and less.
Characteristic clinical symptoms help to recognize the disease in the early stages and avoid these sad consequences:
- Sharp pain after the night's sleep;
- Pain with sharp body spreads or creation of heavy things;
- The body becomes inactive;
- Signs of scoliosis appear;
- The dream gets restless;
- The depressive mood arises;
- Frequent urination is observed.
An independent assessment of these symptoms cannot be correct, as most of them have a common resemblance to signs of other spinal diseases or joints. Therefore, only a rheumatologist or orthopedist has a competence to talk about the presence of the development of osteochondrosis in the lower back.
Classification
Differential diagnosis to correctly determine the disease, distinguish it from identical pathologies and determine the course of treatment, the classification of the stages of this disease helps:
- Step 1 - At this time, the cartilage structure is just starting to change. But now, pathological processes are affected by the roots of nerve endings. As a result, the pain is given in the legs. At the same time, blood flow are born and inflammation is born. The pains are acute or stupid and appear mainly only after reinforced loads on the back shaft;
- The second stage begins with the destruction of the fibrous ring in the spine, while the cartilage is thinner and the vertebrae reduce the distance between them. The pain in the second stage is clear and clear, sometimes irrational. During this period, the mobility of the spine is created along its axis intensifies, there are pitches of nerves, pressure is created in the soft tissues of the muscle spree;
- Stage 3 is characterized by the strong compression of muscle fibers and nerve roots. Unbearable spasms and pain with an ardent character occur. In the area of defeat, numbness looks. With the intensive development of the disease, signs of paresis and paralysis appear;
- Step 4 - The growth period of already formed osteophytes (neoplasms with the bone structure). At this stage, degenerative changes are activated, arthrosis in the spine and joints appear. The back becomes inactive and, in the absence of correct treatment - completely real estate.
Diagnostic methods
As even the ideal knowledge of the clinic and the classification of lumbar spine osteochondrosis does not provide a complete idea of the pathological processes caused by it, a doctor who is involved in the treatment of pathological processes in the spine, diseases of the muscle system or orthopist should be prescribed in additional diagnosis
- X -ray in front and lateral projection - makes it possible to identify axis distortion, osteophyte formation, anatomical abnormalities of vertebrae;
- Magnetic resonance imaging determines the state of the entire zone of damage to the back, detects fragments of destroyed vertebrae, cartilage and inflammation outbreaks;
- Computed tomography provides an idea of the condition of soft tissues, vertebrae bones, the external shell of the intervertebral disc, in principle, which is in principle for its integrity. and blood circulation in the disease location area.
At the same time, the patient tests for a rheumatoid test, general blood indicators, the content of biochemical components. Total research results allow us to accurately establish diagnosis and identify the stage of development of osteochondrosis in the lower back.
Symptoms and treatment of lumbar spine osteochondrosis
Among the common causes of back pain, lumbar spine osteochondrosis, symptoms, whose treatment has its characteristics characteristics. The disease is the early stage of osteochondrosis associated with the process of destruction of the cartilage ring, intervertebral discs, a change in its height towards reduction, swelling and nerve root tweezers. Young and elderly people may face the disease, regardless of gender, social status and religion. A long absence of the manifestation of symptoms of the disease leads to loss of precious time and the transition from a stage of the disease to more serious forms of its development. The main distinctive feature of osteochondrosis is the limit of dystrophic changes in vertebrae tissues, which do not go beyond joint cartilage.
Causes of the early stage of osteochondrosis
Several external and internal factors determine the development of the pathological state of the lumbar region of the axial skeleton. Lumbar osteochondrosis appears due to certain risk factors. These include:
- Body aging after 50 years;
- Inadequate posture and anomaly of the anatomical structure of the axial skeleton, which determines the irregular load in the vertebrae;
- raise weights with a weak muscle structure;
- hypothermia of the patient's body as a whole and the lower back separately;
- Dysfunction of metabolic processes, work of endocrine organs, cardiovascular system;
- Unequal loads in the spine during the performance of production tasks, housework, professional and amateur sports;
- Pathologies of the musculoskeletal system of innate or acquired nature;
- Hypodinamia, high frequency of stressful situations;
- Excessive body weight of the patient;
- Lack of vitamins, minerals, traces elements in the body of a sick person, responsible for the health of the spine;
- Acquisition of high shoes, uncomfortable platforms;
- The use of high pillows and soft mattresses during rest and sleep.
The frequency of osteochondrosis diagnosis of the lumbar skeleton is determined by the number of risk factors for their development that are present in the patient's life.
Disease diagnosis
The determination of the degenerative-distribution lesion of one of the five vertebrae of the axial skeleton lumbar space provides diagnostic measures. They are prescribed by a doctor. In consultation with an expert who knows how to treat lumbar osteochondrosis, a history of the disease is collected, the time and characteristics of the manifestation of signals, the intensity and place of the location of painful sensations are being clarified. The condition of muscle fibers in the damage zone is determined by the visual examination. The use of the palpation method offers an opportunity for a doctor to see an image of the vertebra symmetry and the distance between them. The final diagnosis is established after obtaining the results of additional studies. These include:
- X -ray, held in two projections and offering the opportunity to see the position of the vertebrae, the height of the discs, the plaque seal and bone marginal growth;
- Magnetic resonance imaging, which is a special research method to determine the state of the vascular system and the fibrous rings in the degenerative-distribution lesion zone.
The objectives and methods of treatment of the pathology
The results of diagnostic measures are the basis for the treatment regime for osteochondrosis of the lumbar lumbar skeleton, which seeks certain targets. These include:
- a decrease in pain intensity caused by degenerative-distribution lesions of one or more lumbar skeleton vertebrae;
- Standardization of metabolic processes in cartilage, their restoration and exclusion of the risk of their additional destruction;
- Reduction in load in nerve fibers;
- Increased blood flow in spine tissues using massage, physiotherapeutic procedures;
- Strengthening the muscle structure of the axial skeleton by regular exercise of therapy recommended by the instructor.
Lumbar spine therapy, whose symptoms and treatment have their own characteristics, consists of taking and the use of pharmaceutical products, traditional medicine recipes, unconventional treatment methods, including hirudotherapy. An effective addition to solving the pathology problem is physiotherapeutic, water, massage procedures, gymnastics and sports, including special exercise exercises. Drug therapy includes the use of non -inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, vitamin complexes with elements and minerals.
With very serious pain, novocaine or lidocaine blockages are prescribed, performed by the introduction of injections in the affected vertebrae locations. For local use, ointments, gels, creams, patches with an anti -inflammatory effect of heating and anti -inflammatory. Physiotherapeutic treatment includes the approval of electrophoresis healing courses, diablamic currents, exposure to ultraviolet, manual, shock wave and reflexology. In the absence of positive dynamics, the appearance of hernial protrusions, a surgical operation is prescribed. To avoid the development of complications with the onset of the first symptoms, treatment should begin immediately.
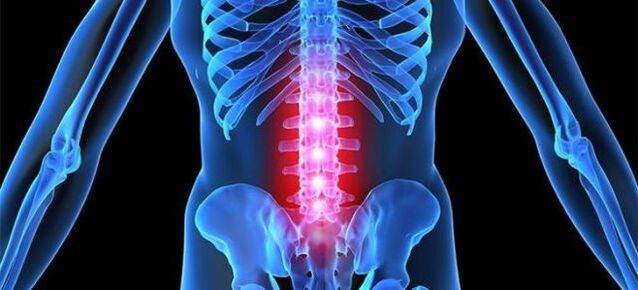
Lumbar osteochondrosis
Lumbar osteochondrosis is one of the most common forms of underlying disease, in fact osteochondrosis. Lumbar osteochondrosis, whose symptoms are equally determined by men and women, manifested in the form of concentrated pain in the sacred area, reflected in their symptoms and lower ends, which is often determined by patients as "tightening the lumbar nerve".
Protrusion for lumbar osteochondrosis
In addition, in this area of interest to us, more often, it is the protrusions that cause the appearance of pain in the lower back. The lumbar region itself, given its location and resources, is more subject to the emergence of certain functional problems. That is, when considering this statement, on the one hand, it can be distinguished that our center of gravity refers directly to the Lumbar Department, respectively, it is precisely that a significant part of cargo accounts. When considering, on the other hand, it can be noted that a significant amplitude of movements, again, falls into this lower back. Given this, the greatest tendency to damage (as well as protrusions of interest to us) is on the concentrated discs in the lower back. Moreover, we should not forget that changes in discs in this and, of course, in other areas, occur, even at the bottom of age -related degenerative processes.
Remember our readers what are the protrusions themselves. The connection of the discs between the column is supplied by the wheels based on the cartilage. The main components of the intervertebral disc are a jetty core and a fibrous ring through which the fixation is supplied within the spinal disc structure. The impact of certain factors and conditions causes the possibility of breaking this ring against the context of which, in turn, the nucleus protrusion occurs. As a result of this process, Hernia develops. As for protrusion, it is already developing as a result of a similar course of the process, but without the concomitant rupture of the ring - in this case, it is simply subject to thinning, not a break, because the core projects directly through the ring. In fact, this protrusion is defined as protrusion.
As for the symptoms of protrusion, it manifests itself as follows:
- a sense of rigidity in the lower back;
- Lumbar pain;
- Lower pain of chronic nature;
- Radiculita Lombosacra;
- Numbness, pain, tingling fingers in the legs, on the feet;
- Impaired urination functions (in rare cases of the pathology into consideration).
Mainly, conservative treatment is applied to lumbar disc protrusion. Meanwhile, significant in the development of protrusion is often accompanied by serious treatment, in this case, you can no longer do without surgical intervention.
Treatment
Especially the treatment of osteochondrosis is multicomponent and quite complicated in its implementation. Mainly all therapy measures are reduced to the following points:
- drug treatment;
- If necessary - surgical treatment;
- diet;
- Medical Physical Education.
Exacerbation of the disease requires, first of all, compliance with patient rest. The main recommendation for this part is a hard/hard place. Extremely expressed in demonstrations, the attacks provide for the need for a minimum engine load and early contact to the relevant expert.






















